[vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
Kuwait
Kuwait was the 56th largest economy in the world by nominal GDP in 2018. Its GDP per capita was $34,244 USD. It is situated on the Persian Gulf bordering Iraq and Saudi Arabia. It had the seventh largest proven oil reserves in the world in 2018. It was ranked 57th in the Economic Complexity Index in 2017. It is a member of the GCC and OPEC. Services was the largest economic sector in 2017 (59 percent of GDP), followed by manufacturing (7 percent), and agriculture (0.51 percent). In 2017, the largest export sectors were minerals (79 percent), services (9.07 percent), and chemicals (6.75 percent). The largest individual exports were crude oil (62 percent), refined petroleum (13 percent), and ICT services (4.9 percent). Its largest export partners were South Korea (17.2 percent), China (16.04 percent), India (11.3 percent), and Japan (10.6 percent). The largest goods imports were transmission apparatus for radio, telephones, and television (7.14 percent), and cars (6.61 percent). By the 19th century, Kuwait had become an important trading and pearling centre in the gulf region. Fearing an increase in Ottoman control, it became a British protectorate in 1899. After World War One, Ibn Saud attempted to capture Kuwait but after failing he imposed a trade blockade that lasted until 1937. Under the blockade and the Great Depression the economy suffered. In 1938, oil was discovered transforming the economy. The government used its new wealth to invest in infrastructure and to establish two key funds. In 1953, it established the world's first sovereign wealth fund, now called the Kuwait Investment Authority. And in 1961, it established a regional development fund, the Kuwait Fund for Arab Economic Development, which has now expanded its aid to over 100 countries. In 1961, Kuwait became an independent country as the British withdrew from the gulf states. The oil and gas industry were nationalised in 1975. The economy suffered during the early 1980s as the oil price fell, the 1982 Souk al-Manakh stock market crash, and the impact from the Iran-Iraq war. Similarly, the economy suffered in 1990 and 1991 after Iraq invaded in 1990. Following liberation, the economy rebounded and grew strongly in the 2000s as the oil price recovered. After the drop in the oil price in 2014-2015, the budget came under pressure. The government responded by further cuts to fuel and electricity subsidies and by agreeing with other GCC members to introduce an excise tax on tobacco and alcohol and a VAT. In 2017, the government launched the "New Kuwait Vision 2035" development plan. The plan aims to further diversify the economy building on earlier development plans.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]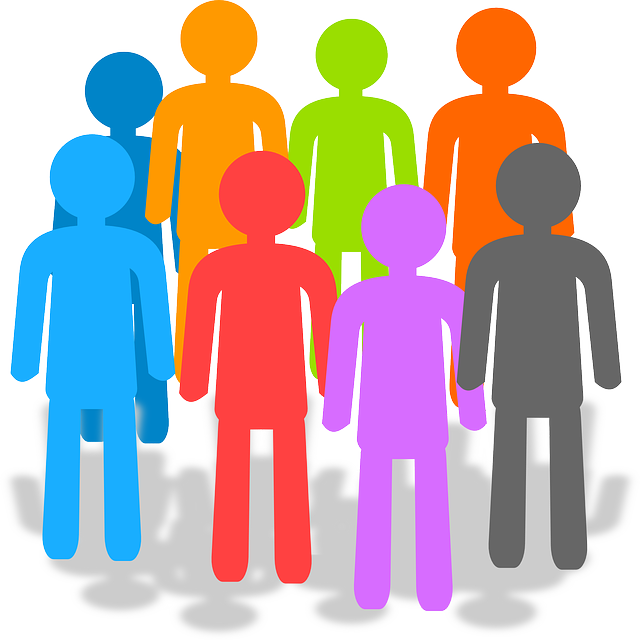 Its population in 2018 was 4,197,128 [1]
Its population in 2018 was 4,197,128 [1]
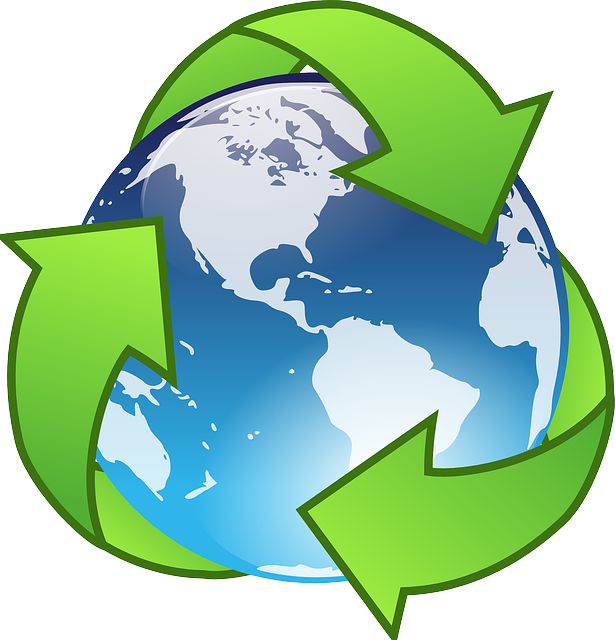 In 2015, 0.00% of its total energy
In 2015, 0.00% of its total energy
consumption was renewable [2]
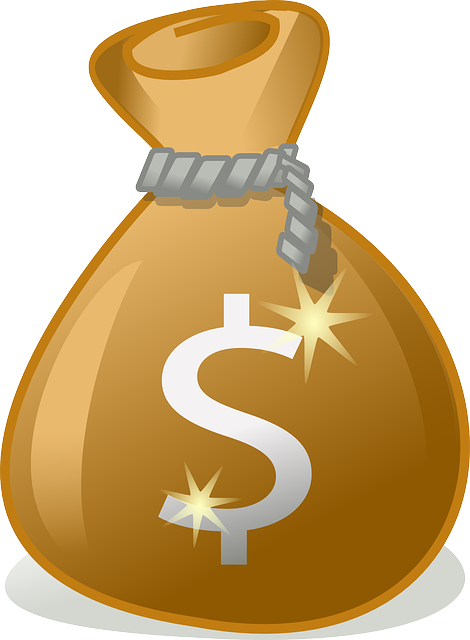 In 2021, its GDP grew by 0.00% [2]
In 2021, its GDP grew by 0.00% [2]
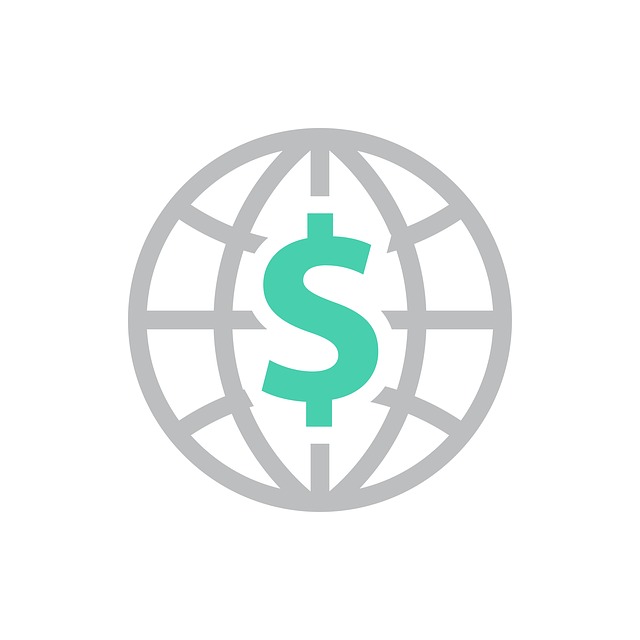 In 2021 it had a positive Current
In 2021 it had a positive Current
Account Balance of US$bn 21.73 [3]
 Its unemployment rate in 2021 was 1.28% [3]
Its unemployment rate in 2021 was 1.28% [3]
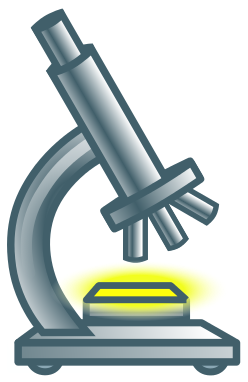 Its Expenditure on R&D (as a percentage of
Its Expenditure on R&D (as a percentage of
GDP) in 2020 was 0.19% [2]
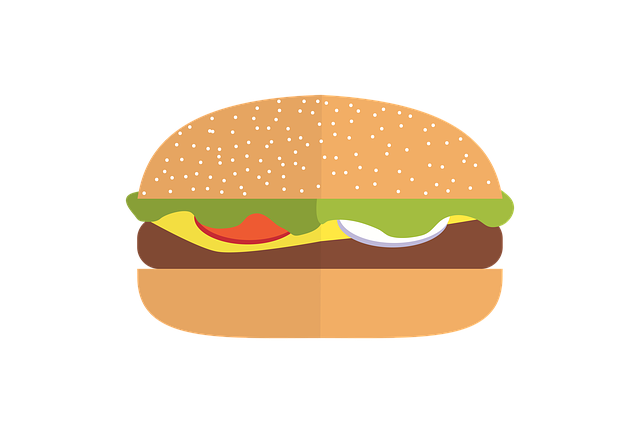 A Big Mac will set you back the
A Big Mac will set you back the
local equivalent of US$3.46 [4]
What free trade areas or economic unions is it a member of?
Member of the Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf (GCC) since 25/05/1981
Other members:
Bahrain, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates
What trade deals are there between Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf and other countries and economic unions?
Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) - Singapore free trade agreement (from 01/11/2013)
EFTA - Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Free Trade Agreement (from 01/07/2014)
EFTA - Gulf Cooperation Council free trade agreement (from 01/07/2014)
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]What trade deals are there with other countries and economic unions?
Pan-Arab Free Trade Area (from 01/01/1998)
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]Unerring Drive and Determination Pay Off for Kuwait’s Stock Exchange
Digital Transformation Shapes the Future of AUB
stc: High Ideals, and a Series of Firsts for Kuwait
Balsam Al-Ayoub: Cut and Thrust for Multi-talented Philanthropist
Ahmed Attiga: The Enviable CV and Impressive Performance of APICORP Chief
A New Era for Kuwait International Bank: Architecting the Future of Technology-based Banking
Gulf Insurance Group-Kuwait: A History of Firsts and a Booming ‘GIG’ Economy for Leader in Insurance
First Qatar: A Development Company Casting Pearls on Doha’s Golden Beaches
KIB – More than a Bank: A Partner for Life with Customer Interests at its Heart
Bahrain Minister of Industry, Commerce, and Tourism Zayed Bin Rashid Al Zayani: Maintaining and Expanding a Leading Edge
Trade with the United Kingdom
Source: UK Office for National Statistics, October 2022.
Contains public sector information licensed under the Open Government Licence v3.0.
























































































