[vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
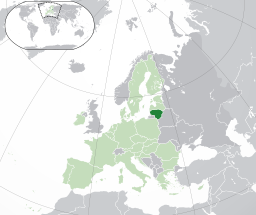
Lithuania
The light green area is the rest of the European Union
Lithuania was the 82nd largest economy in the world by nominal GDP in 2018. GDP per capita is $19,090 USD. It is the largest economy in the Baltics. It is ranked 37th in the World Bank's Human Capital Index, and trade was at 162 percent of GDP in 2018. Its economy is also diverse with a ranking of 34th in the Economic Complexity Index (2017). It is a member of the EU and OECD. Services was the largest economic sector in 2018 (61 percent of GDP), followed by manufacturing (17 percent), and agriculture (2.7 percent). In 2017, the largest export sectors were services (24 percent), agricultural (18 percent), chemicals (12.6 percent), minerals (11.3 percent), machinery (9 percent), and textiles (8.7 percent). The largest individual exports were transport services (14 percent), refined petroleum (10 percent), and ICT services (6.45 percent). Its largest export partners were Russia (14.9 percent), Latvia (9.5 percent), Poland (7.9 percent), and Germany (6.7 percent). The largest goods imports were crude oil (12 percent), cars (3.5 percent), and refined petroleum (3 percent). Lithuania regained its independence in 1918 after World War One. During World War Two it was invaded by the Soviets, Germans, and Soviets again. Under Soviet control, the mainly agricultural economy was industrialised with an emphasis on heavy industry. Lithuania was the first country to declare independence from the Soviet Union in 1990 and rapidly transitioned from a centrally planned to a market economy. Macroeconomic stabilisation policies, privatisation, and its own stable currency led to an open and rapidly growing economy. As a result Lithuania became known as a "Baltic Tiger". Foreign investment and EU funding aided in the transition. Lithuania joined the WTO in 2001, the EU in 2004, the euro zone in 2015, and the OECD in 2018. The economy was severely hit by the 2008-09 global financial crisis, but it has recovered to be one of the fastest growing in Europe. The economy benefits from levels of participation in tertiary education above the OECD average.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text] Its population in 2018 was 2,876,475 [1]
Its population in 2018 was 2,876,475 [1]
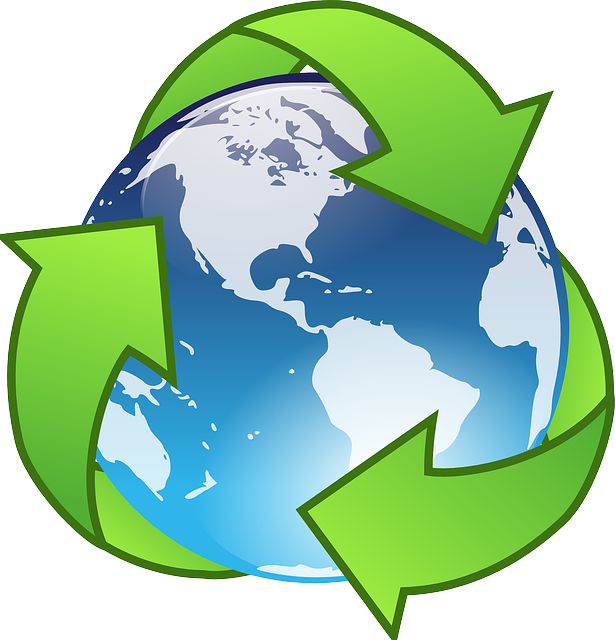 In 2015, 28.96% of its total energy
In 2015, 28.96% of its total energy
consumption was renewable [2]
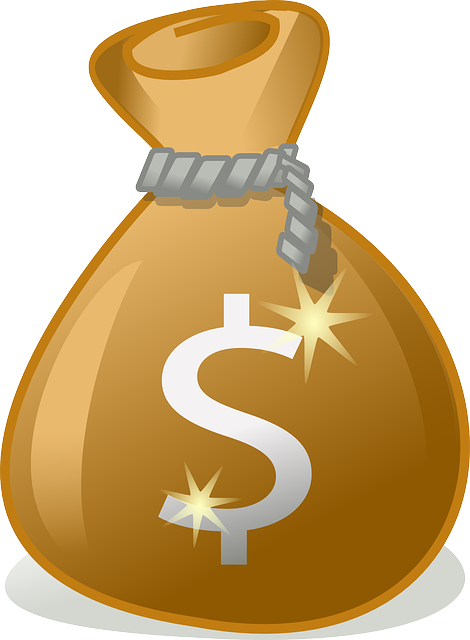 In 2021, its GDP grew by 5.00% [2]
In 2021, its GDP grew by 5.00% [2]
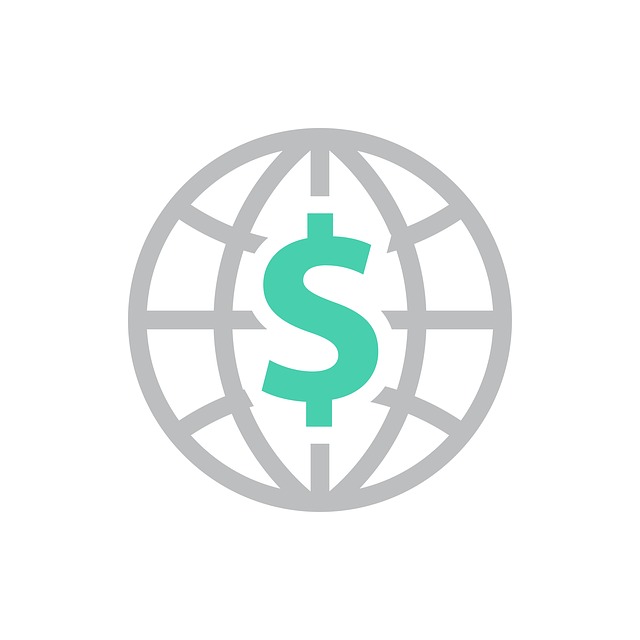 In 2021 it had a positive Current
In 2021 it had a positive Current
Account Balance of US$bn 1.77 [3]
 Its unemployment rate in 2021 was 7.12% [3]
Its unemployment rate in 2021 was 7.12% [3]
 Its Expenditure on R&D (as a percentage of
Its Expenditure on R&D (as a percentage of
GDP) in 2020 was 1.16% [2]
What free trade areas or economic unions is it a member of?
Member of the European Union (EU) since 01/05/2004
Other members:
Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden
What trade deals are there between European Union and other countries and economic unions?
EU - Andorra Customs Union (from 01/01/1991)
European Single Market (SM) (from 01/01/1993)
EU - Sri-Lanka Co-operation and Partnership Agreement (from 01/04/1995)
EU - Türkiye Customs Union (from 31/12/1995)
EU - Faroe Islands Agreement (from 01/01/1997)
EU - Palestinian Authority Interim Association Agreement (from 01/07/1997)
EU - Tunisia Association Agreement (from 01/03/1998)
EU - Armenia Partnership and Cooperation Agreement (from 09/09/1999)
EU - Morocco Association Agreement (from 01/03/2000)
EU - Israel Association Agreement (from 01/06/2000)
EU - Mexico Global Agreement (from 01/10/2000)
EU - San Marino Customs Union (from 01/04/2002)
EU - Jordan Association Agreement (from 01/05/2002)
EU - North Macedonia Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/04/2004)
EU - Pakistan Co-operation agreement (from 29/04/2004)
EU - Egypt Association Agreement (from 01/06/2004)
EU - Chile Association Agreement and Additional Protocol (from 01/03/2005)
EU - Algeria Association Agreement (from 01/09/2005)
EU - Lebanon Association Agreement (from 01/04/2006)
EU - Albania Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/04/2009)
EU - Pacific States Interim EPA (from 20/12/2009)
EU - Montenegro Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/05/2010)
EU - Central America Association Agreement (from 01/08/2013)
EU - Serbia Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/09/2013)
EU - Bosnia and Herzegovina Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/06/2015)
EU - South Korea Free Trade Agreement (from 01/07/2015)
EU - Kosovo Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/04/2016)
EU - Georgia Association Agreement (from 01/07/2016)
EU - Moldova Association Agreement (from 01/07/2016)
EU - Canada Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA) (from 21/09/2017)
EU - Eswatini (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Lesotho (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Mozambique (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Namibia (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - South Africa Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Botswana (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Japan Economic Partnership Agreement (from 01/02/2019)
EU - Eastern and Southern Africa States free trade agreement (from 07/02/2019)
UK - EU Trade Deal (from 01/01/2021)
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]What trade deals are there with other countries and economic unions?
None
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]Reitan Convenience: Value-Based Leadership to Drive Sustainability Effort
Russia – Moving Borders Politely
Trade with the United Kingdom
Source: UK Office for National Statistics, October 2022.
Contains public sector information licensed under the Open Government Licence v3.0.
Loading, Please Wait!
This may take a second or two.