[vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
Czechia
The light green area is the rest of the European Union
Czechia was the 44th largest economy in the world by nominal GDP in 2018. GDP per capita is $23,078 USD. It is a well-developed and open economy. Czechia is ranked 14th in the World Bank's Human Capital Index, and trade was at 150 percent of GDP in 2018. Its economy is also diverse with a ranking of 9th in the Economic Complexity Index (2017). It is a member of the EU and OECD. Services was the largest economic sector in 2018 (56 percent of GDP), followed by manufacturing (23 percent), and agriculture (1.9 percent). In 2017, the largest export sectors were machinery (20 percent), vehicles (19 percent), electronics (14.3 percent), services (13.2 percent), and chemicals (8.59 percent). The largest individual exports were cars (10 percent), car parts (7.1 percent), ICT services (6.33 percent), computers (3.7 percent), and travel and tourism (3.4 percent). Its largest export partners were Germany (31 percent), Slovakia (7.8 percent), and Poland 6.12 percent. The largest goods imports were parts of motor vehicles (5.6 percent), parts and accessories for office machines (4.97 percent), and transmission apparatus for radio, telephone, and TV (4.25 percent). Czechoslovakian industry was already well developed by the start of World War Two and survived the war largely intact. Following the fall of communism in 1989 and the dissolution of Czechoslovakia in 1993, Czechia took advantage of its large established industrial base and central location by increasing foreign investment. It quickly became a key country in the global supply chain for cars and other manufactured goods. Growth was interrupted by the global financial crisis but had recovered by 2015. Since 2014, the government has introduced reforms to further increase investment and welfare, and to decrease corruption and tax evasion. The government also plans to reform the labour market in order to address labour shortages resulting from low unemployment and labour market rigidities.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text] Its population in 2018 was 10,625,250 [1]
Its population in 2018 was 10,625,250 [1]
 In 2015, 14.83% of its total energy
In 2015, 14.83% of its total energy
consumption was renewable [2]
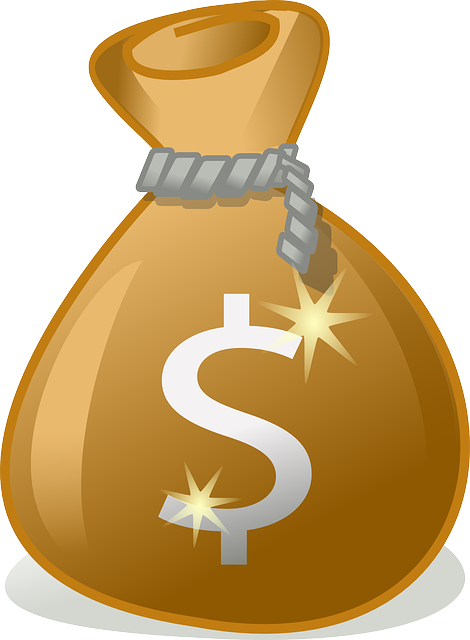 In 2021, its GDP grew by 3.34% [2]
In 2021, its GDP grew by 3.34% [2]
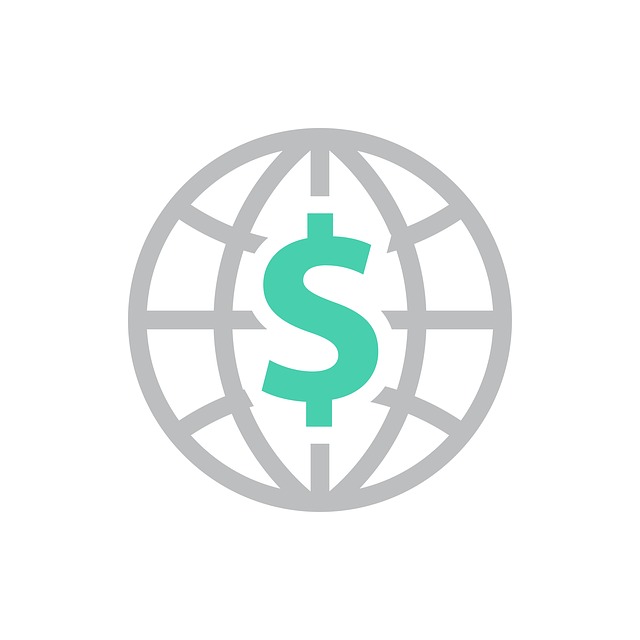 In 2021 it had a negative Current
In 2021 it had a negative Current
Account Balance of US$bn 2.23 [3]
 Its unemployment rate in 2021 was 2.82% [3]
Its unemployment rate in 2021 was 2.82% [3]
 Its Expenditure on R&D (as a percentage of
Its Expenditure on R&D (as a percentage of
GDP) in 2020 was 1.99% [2]
 A Big Mac will set you back the
A Big Mac will set you back the
local equivalent of US$3.81 [4]
What free trade areas or economic unions is it a member of?
Member of the European Union (EU) since 01/05/2004
Other members:
Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden
What trade deals are there between European Union and other countries and economic unions?
EU - Andorra Customs Union (from 01/01/1991)
European Single Market (SM) (from 01/01/1993)
EU - Sri-Lanka Co-operation and Partnership Agreement (from 01/04/1995)
EU - Türkiye Customs Union (from 31/12/1995)
EU - Faroe Islands Agreement (from 01/01/1997)
EU - Palestinian Authority Interim Association Agreement (from 01/07/1997)
EU - Tunisia Association Agreement (from 01/03/1998)
EU - Armenia Partnership and Cooperation Agreement (from 09/09/1999)
EU - Morocco Association Agreement (from 01/03/2000)
EU - Israel Association Agreement (from 01/06/2000)
EU - Mexico Global Agreement (from 01/10/2000)
EU - San Marino Customs Union (from 01/04/2002)
EU - Jordan Association Agreement (from 01/05/2002)
EU - North Macedonia Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/04/2004)
EU - Pakistan Co-operation agreement (from 29/04/2004)
EU - Egypt Association Agreement (from 01/06/2004)
EU - Chile Association Agreement and Additional Protocol (from 01/03/2005)
EU - Algeria Association Agreement (from 01/09/2005)
EU - Lebanon Association Agreement (from 01/04/2006)
EU - Albania Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/04/2009)
EU - Pacific States Interim EPA (from 20/12/2009)
EU - Montenegro Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/05/2010)
EU - Central America Association Agreement (from 01/08/2013)
EU - Serbia Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/09/2013)
EU - Bosnia and Herzegovina Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/06/2015)
EU - South Korea Free Trade Agreement (from 01/07/2015)
EU - Kosovo Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/04/2016)
EU - Georgia Association Agreement (from 01/07/2016)
EU - Moldova Association Agreement (from 01/07/2016)
EU - Canada Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA) (from 21/09/2017)
EU - Eswatini (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Lesotho (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Mozambique (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Namibia (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - South Africa Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Botswana (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Japan Economic Partnership Agreement (from 01/02/2019)
EU - Eastern and Southern Africa States free trade agreement (from 07/02/2019)
UK - EU Trade Deal (from 01/01/2021)
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]What trade deals are there with other countries and economic unions?
None
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]The View From Belgium: Top Banker Pleads for Caution
IFC: Ukrainian Refugees Access Finance via New Digital Data Corridors
Generali Investments CEE: Leading by Example, with Proximity to Clients and a Firm Sustainability Focus
Generali´s Josef Beneš Takes Decisions with Care Based on a Century of Experience
KBC Asset Management with CEO Johan Lema: ‘Everyone Invested’ Strategy Has Taken Belgian Firm to Prominence
How Do We Measure Social Impact? UniCredit’s SIB Unit Has an Answer
Building Bridges: Joining Impact Investing and Social Entrepreneurship
Europe: Fig Leaves to Save Spain and Italy
CFI.co Meets the Group CEO of KBC: Johan Thijs
CFI.co Meets the CEO of Hellenic Bank: Bert Pijls
Trade with the United Kingdom
Source: UK Office for National Statistics, October 2022.
Contains public sector information licensed under the Open Government Licence v3.0.