[vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
China
China's economy is the second largest in the world by nominal GDP. In 2018, it was around two-thirds of the US economy and 2.7 times larger than Japan, the third largest. China has been among the fastest growing economies over the last 30 years, averaging over 6 percent annually. It is also the world's fastest-growing consumer market and second-largest importer of goods. It has 119 of the world's 500 largest companies, the world's largest foreign-exchange reserves, and the second-highest number of billionaires with total wealth of $996 billion. It still has much further to grow with a GDP per capita of $9,771 USD in 2018 and a Human Capital Index rating of 46. Services is the largest sector at 52 percent of GDP, followed by manufacturing at 29.4 percent. It is the world's largest manufacturing economy and exporter of goods. It also has the world's largest natural resources worth $23 trillion, 90 percent of which are coal and rare earth metals. In 2017, its main export sectors were electronics (27 percent of total exports), machinery (22 percent), and textiles (15 percent). Its largest individual exports were transmitting and receiving apparatus for televisions, radio and phones (8.5 percent), computers (5.3 percent), ICT services (4.7 percent), and parts and accessories for office machines (3.4 percent). Its largest export partner is the US (19 percent). Its largest imports are electronic integrated circuits (13.2 percent), oil (9.9 percent), iron ore (3.9 percent), cars (2.9 percent) and soya beans (2.3 percent). Since the late 1970s, China has moved from a closed, centrally planned system based on agriculture to a more market-oriented system based on manufacturing exports and services. In 1985 about 63 percent of the population lived in rural areas, and nearly 63 percent of the labour force was in agriculture. Today 59 percent live in urban areas and 43 percent work in services. Reforms began with the end of collectivized agriculture in the late 1970s and early 1980s. Reform then moved to other parts of the economy with liberalisation of prices and greater autonomy for SOEs. The private sector was encouraged, and a modern banking system and stock markets were developed. China employed a selective industrial policy with state support for key sectors and maintained a restrictive investment regime. Its latest strategic plan, "Made in China 2025", seeks to put China at the forefront of a range of key global industries.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text] Its population in 2018 was 1,415,045,928 [1]
Its population in 2018 was 1,415,045,928 [1]
 In 2015, 12.41% of its total energy
In 2015, 12.41% of its total energy
consumption was renewable [2]
 In 2021, its GDP grew by 8.11% [2]
In 2021, its GDP grew by 8.11% [2]
 In 2021 it had a positive Current
In 2021 it had a positive Current
Account Balance of US$bn 317.30 [3]
 Its unemployment rate in 2021 was 3.96% [3]
Its unemployment rate in 2021 was 3.96% [3]
 Its Expenditure on R&D (as a percentage of
Its Expenditure on R&D (as a percentage of
GDP) in 2020 was 2.40% [2]
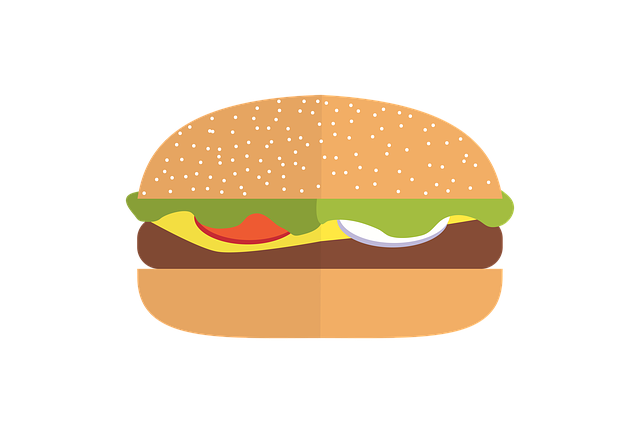 A Big Mac will set you back the
A Big Mac will set you back the
local equivalent of US$3.05 [4]
What free trade areas or economic unions is it a member of?
None
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]What trade deals are there with other countries and economic unions?
Asia Pacific Trade Agreement (from 17/06/1976)
China - Hong Kong, China, free trade agreement (from 29/06/2003)
China - Macao, China, free trade agreement (from 17/10/2003)
Chile - China free trade agreement (from 01/10/2006)
Pakistan - China free trade agreement (from 01/07/2007)
China - New Zealand free trade agreement (from 01/10/2008)
China - Singapore free trade agreement (from 01/01/2009)
ASEAN - China Free Trade Area (from 01/01/2010)
Peru - China free trade agreement (from 01/03/2010)
China - Costa Rica free trade agreement (from 01/08/2011)
Iceland - China free trade agreement (from 01/07/2014)
Switzerland - China free trade agreement (from 01/07/2014)
Australia - China free trade agreement (from 20/12/2015)
China - Korea, Republic of, free trade agreement (from 20/12/2015)
China - Georgia free trade agreement (from 18/01/2018)
China - Mauritius free trade agreement (from 01/01/2021)
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]Ageas CEO Hans de Cuyper: Ensuring a Sustainable Future for the Insurance Industry
ICBC Dubai (DIFC) Branch: Innovate to Differentiate
VIA optronics AG: Challenged by Optics or Display Issues? VIA’s Got This One Covered
Jürgen Eichner: Vision of VIA optronics Boss Takes Company on Whirlwind Trajectory
A Bipolar World? Searching in Vain for a Dollar Alternative
Otaviano Canuto: Some Economies May Soon Face a Hard Landing
Lord Waverley: First In, Best Dressed — UK’s Bid to Join Key Regional Trade Agreement
The Great Dictator Becomes More and More Isolated
Fortress Russia on Shaky Ground: EU Finds Its Footing and Unleashes Its Economic Might
Market Volatility as Push (Slowly) Comes to Shove: Grappling with a Multitude of Crises in an Increasingly Dangerous World
Trade with the United Kingdom
Source: UK Office for National Statistics, October 2022.
Contains public sector information licensed under the Open Government Licence v3.0.