[vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
Zambia
Zambia was the 103rd largest economy in the world by nominal GDP in 2018. Its GDP per capita was $1,540 USD. It is Africa's second-largest copper producer. It achieved middle-income country status in 2011 following a decade of strong economic growth. It was ranked 131st in the World Bank's Human Capital Index and 78th in the Economic Complexity Index in 2017. It is a member of the Southern African Development Community and the African Union. Services was the largest economic sector in 2018 (54 percent of GDP), followed by manufacturing (8.5 percent), and agriculture (2.6 percent). In 2017, the largest export sectors were metals (72.5 percent), services (11.36 percent), and agriculture (8.8 percent). The largest individual exports were unrefined copper (49.9 percent), refined copper and copper alloys (19.17 percent), and travel and tourism (8.6 percent). Its largest export partners were China (44 percent), India (13.64 percent), and the UAE (6.53 percent). The largest goods imports were copper ore (9.87 percent), cobalt oxides and hydroxides (8.34 percent), refined petroleum (5.43 percent), and crude oil (5.03 percent). In 1889, the British took control of the area with the establishment of the British South Africa company. In 1911, Northern Rhodesia was created by the merger of two smaller protectorates. The Crown took control in 1924. In 1928, the first commercial copper mine was opened spurring development in the country. After WW2 and a brief federation with Southern Rhodesia (Zimbabwe) and Nyasaland (Malawi), the country gained independence in 1964. The economy grew strongly in the 1960s and 1970s on the back of copper mining. But a fall in copper prices from the mid-1970s and the oil shocks ended the period of growth. A further fall in the copper price in the 1980s combined with drought and economic mismanagement resulted in just two years of growth during the 1980s. Reforms in the 1990s laid the foundation for growth in the 2000s.The increase in the copper price in the 2000s also contributed. Real GDP growth averaged 6.6 percent between 1999 and 2014. With the fall in the copper price in 2015, growth has slowed.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text] Its population in 2018 was 17,609,178 [1]
Its population in 2018 was 17,609,178 [1]
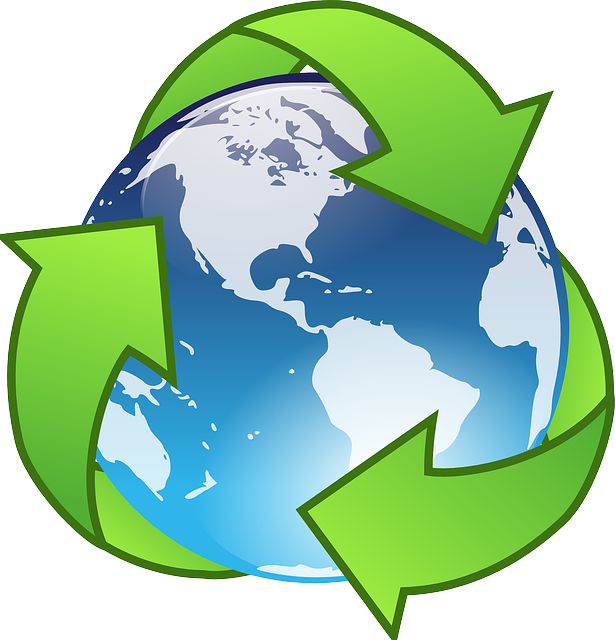 In 2015, 87.99% of its total energy
In 2015, 87.99% of its total energy
consumption was renewable [2]
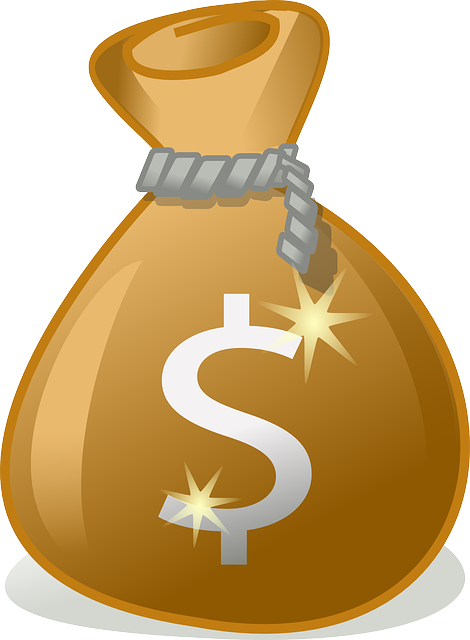 In 2021, its GDP grew by 3.57% [2]
In 2021, its GDP grew by 3.57% [2]
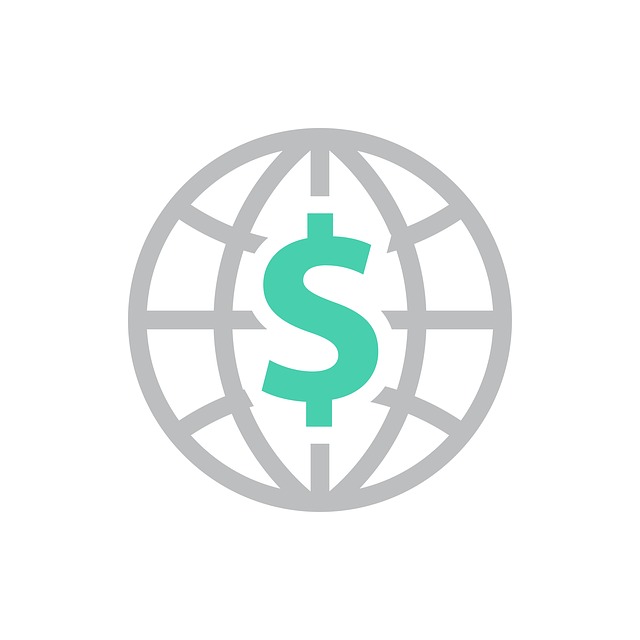 In 2021 it had a positive Current
In 2021 it had a positive Current
Account Balance of US$bn 1.40 [3]
What free trade areas or economic unions is it a member of?
None
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]What trade deals are there with other countries and economic unions?
Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (from 08/12/1994)
Southern African Development Community (from 01/09/2000)
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]Obituary – Wilbur Addison Smith (1933-2021): Lion of African Literature
Bank One: Supporting Mauritius’ Efforts to Emerge as a Private Wealth Hub for Africa
Africa – Unity Key to Remarkable Success in Fighting Covid-19
PwC: Nigerian Report on Ease of Doing Business
CFI.co Meets the CEO of ARC Ltd: Dolika Banda
Dambisa Moyo: Looking From a Unique Angle
Zambia Set to Impress and Welcome Investors
Back to Africa – Chibwe Masabo Henry: The Diaspora as a Driver of Development
Our Hero Justina Mutale: Postive Runway
EDFI: Africa and Energy Access – Financing Impact
Trade with the United Kingdom
Source: UK Office for National Statistics, October 2022.
Contains public sector information licensed under the Open Government Licence v3.0.
Loading, Please Wait!
This may take a second or two.