[vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
Netherlands
The light green area is the rest of the European Union
The Netherlands was the 17th largest economy in the world by nominal GDP in 2018. GDP per capita is $53,024 USD which is above the average for the OECD and High Income countries. It is an important transport hub for Europe with Rotterdam being the largest port in Europe and Amsterdam among the biggest airports. It is an open economy with a long history of innovation in finance and trade, including the first stock market. It is ranked 6th on the World Bank's Logistics Performance Index. Trade was at 158 percent of GDP in 2018. It is ranked 8th in the World Bank's Human Capital Index and 18th in the Economic Complexity Index (2017). It is a member of the EU, OECD, and the Benelux union with Belgium and Luxembourg. Services was the largest economic sector in 2018 (70 percent of GDP), followed by manufacturing (11.1 percent), and agriculture (1.63 percent). In 2017, the largest export sectors were services (24.3 percent), agriculture (15.4 percent), chemicals (14.97 percent), and machinery (14.7 percent). The largest individual exports were ICT services (16.4 percent), refined petroleum (6.1 percent), and transport services (4.55 percent). Its largest export partners were Germany (20 percent), Belgium (13.3 percent), the UK (9.2 percent), and France (7.7 percent). The largest goods imports were crude oil (7.6 percent), refined petroleum (7.16 percent), transmission apparatus for radio, telephone, and television (4.13 percent), and computers (3.1 percent). During the 1600s, the Dutch economy grew rapidly and built a maritime trading empire. It was a "Golden age" of trade, innovation, and art. War in the 1700s, French occupation between 1795 and 1810, and vested economic interests led to a slowdown in growth and innovation until industrialisation. From the 1860s the economy industrialised rapidly with the development of railroads, textiles, and food processing. The country was neutral during World War One but suffered from the decline in trade. The economy was ravaged by World War Two but recovered strongly through the US Marshall Plan, fiscal prudence, low wages, and increased capital intensity. The discovery of natural gas in 1959 boosted the economy but also led to an increase in government spending and the stagnation of other industries in the 1970s which left the economy vulnerable to the 1970s oil shocks. The early 80s saw recession and unemployment before fiscal reform, wage moderation, and labour market reforms helped the economy to recover. Between 1996 and 2000, economic growth was well above the European average and the turnaround from the 1980s was being described as a "miracle". Growth slowed down in 2001 as part of the global economic slowdown, recovered in 2006 and 2007, before being hit by the global financial crisis. Further government reforms saw the economy recover in 2014 and in 2019 the country was ranked as the most competitive in Europe by the World Economic Forum.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text] Its population in 2018 was 17,084,459 [1]
Its population in 2018 was 17,084,459 [1]
 In 2015, 5.89% of its total energy
In 2015, 5.89% of its total energy
consumption was renewable [2]
 In 2021, its GDP grew by 5.04% [2]
In 2021, its GDP grew by 5.04% [2]
 In 2021 it had a positive Current
In 2021 it had a positive Current
Account Balance of US$bn 96.30 [3]
 Its unemployment rate in 2021 was 4.23% [3]
Its unemployment rate in 2021 was 4.23% [3]
 Its Expenditure on R&D (as a percentage of
Its Expenditure on R&D (as a percentage of
GDP) in 2020 was 2.29% [2]
What free trade areas or economic unions is it a member of?
Member of the European Union (EU) since 25/03/1957
Other members:
Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden
What trade deals are there between European Union and other countries and economic unions?
EU - Andorra Customs Union (from 01/01/1991)
European Single Market (SM) (from 01/01/1993)
EU - Sri-Lanka Co-operation and Partnership Agreement (from 01/04/1995)
EU - Türkiye Customs Union (from 31/12/1995)
EU - Faroe Islands Agreement (from 01/01/1997)
EU - Palestinian Authority Interim Association Agreement (from 01/07/1997)
EU - Tunisia Association Agreement (from 01/03/1998)
EU - Armenia Partnership and Cooperation Agreement (from 09/09/1999)
EU - Morocco Association Agreement (from 01/03/2000)
EU - Israel Association Agreement (from 01/06/2000)
EU - Mexico Global Agreement (from 01/10/2000)
EU - San Marino Customs Union (from 01/04/2002)
EU - Jordan Association Agreement (from 01/05/2002)
EU - North Macedonia Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/04/2004)
EU - Pakistan Co-operation agreement (from 29/04/2004)
EU - Egypt Association Agreement (from 01/06/2004)
EU - Chile Association Agreement and Additional Protocol (from 01/03/2005)
EU - Algeria Association Agreement (from 01/09/2005)
EU - Lebanon Association Agreement (from 01/04/2006)
EU - Albania Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/04/2009)
EU - Pacific States Interim EPA (from 20/12/2009)
EU - Montenegro Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/05/2010)
EU - Central America Association Agreement (from 01/08/2013)
EU - Serbia Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/09/2013)
EU - Bosnia and Herzegovina Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/06/2015)
EU - South Korea Free Trade Agreement (from 01/07/2015)
EU - Kosovo Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/04/2016)
EU - Georgia Association Agreement (from 01/07/2016)
EU - Moldova Association Agreement (from 01/07/2016)
EU - Canada Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA) (from 21/09/2017)
EU - Eswatini (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Lesotho (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Mozambique (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Namibia (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - South Africa Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Botswana (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Japan Economic Partnership Agreement (from 01/02/2019)
EU - Eastern and Southern Africa States free trade agreement (from 07/02/2019)
UK - EU Trade Deal (from 01/01/2021)
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]What trade deals are there with other countries and economic unions?
None
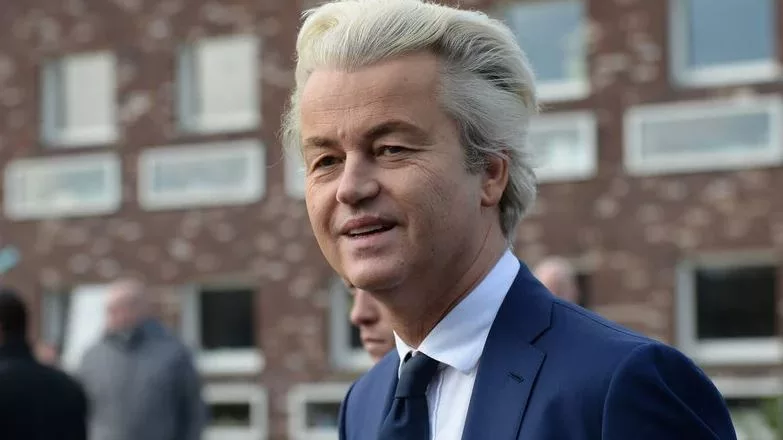
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]Political Upset in The Netherlands: Voters Turn to Firebrand Leader
Right Place, Right Time, Right Attitude: Dutch Firm, Orange Capital Partners Plays Its Cards with Skill
TANQIA: Blueprint for Sustainable Treatment is Blazing Trails in Water-Strapped Region
Double Dip Recession in the Making, UK Expected to Emerge First
Rainmaker: Revolutionary Water Supply Solutions That Are Needed Now More Than Ever
Uruguay: A Near-Perfect Country to Live, Work, and Play Post-Covid-19
EU Prime Ministers Beat a Path to The Hague
Europe: Fig Leaves to Save Spain and Italy
Resistance Is Futile as Berlin Backs EU Solidarity
Few Strings in US, Many in Europe
Trade with the United Kingdom
Source: UK Office for National Statistics, October 2022.
Contains public sector information licensed under the Open Government Licence v3.0.

























































































