[vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
Afghanistan
Afghanistan was the 113th largest economy by nominal GDP in 2018. GDP per capita was $521 USD. The economy has suffered from over forty years of war. It was ranked 133rd in the World Bank's Human Capital Index. Services accounted for 52.7 percent of GDP in 2017, followed by agriculture (20.5 percent), and manufacturing (11.1 percent). The largest export sectors in 2017 were agriculture (46.2 percent), services (29.5 percent), and minerals (8.11 percent). The largest individual exports were ICT services (24 percent), grapes (9.96 percent), natural gum and resin (6.8 percent), figs (6.8 percent), and gold (5.3 percent). Its largest export partners were Pakistan (40.9 percent), India (39 percent), and the UAE (9.74 percent). The largest import goods were transmission apparatus for radios, telephones, and televisions (8.77 percent), refined petroleum (6.4 percent), cigars and cigarettes (4.17 percent), and wheat or meslin flour (3.97 percent). Afghanistan was founded in 1747 after the Pashtun tribes united against the other ethnic groups. They maintained their dominance until the civil war after the Soviet withdrawal. During the 18th and 19th centuries Afghanistan served as a buffer between British and Russian interests. In 1919, the country gained independence from the British after the third Anglo-Afghan war. King Amanullah began to modernise the economy but fled in 1929 after a series of revolts. In the years that followed, the British, Soviets, and Americans jockeyed for influence. In the 1950s and 1960s, further attempts were made to modernise the country. In 1973 a coup deposed the Monarchy and established a republic. The government began to target leftist groups fearing growing Soviet influence. The communists take power in 1978 following another coup. When the communist government looked in trouble, the Soviets invaded in 1979. The Soviets fought a bitter war with the internationally backed mujahidin rebels. They withdrew in 1989. Following the Russian withdrawal, the country descended into civil war. In 1994, the Taliban emerged, capturing Kabul in 1996. The Taliban are mostly made up of Pashtun Islamic extremists. Following the September 11 terrorist attacks, a US led coalition invaded Afghanistan, after the Taliban refused to hand over the mastermind of the attacks, Osama Bin Laden. In 2004, free elections were held. With international aid and investment from the diaspora, the economy grew during the 2000s. Real GDP growth averaged 9 percent between 2003 and 2013. The Taliban have regained strength in recent years and have been waging terrorism against the state. The US began negotiating with the Taliban in late 2018 with the aim of securing peace. The Trump administration has promised the American public that it will withdraw troops from Afghanistan. Despite improvements in incomes, health and education since 2001, Afghanistan remains extremely poor and dependent on foreign aid.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]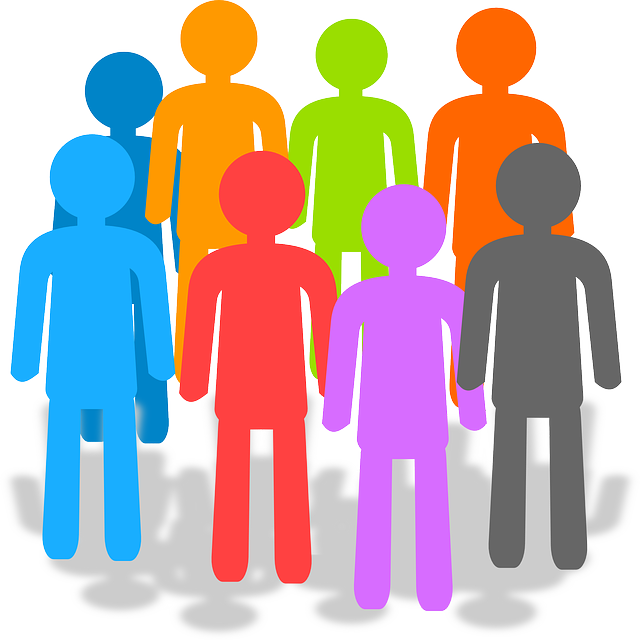 Its population in 2018 was 36,373,176 [1]
Its population in 2018 was 36,373,176 [1]
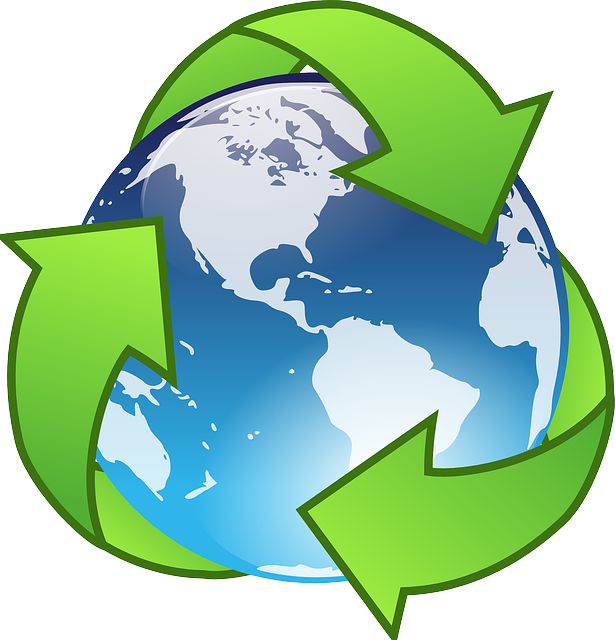 In 2015, 18.42% of its total energy
In 2015, 18.42% of its total energy
consumption was renewable [2]
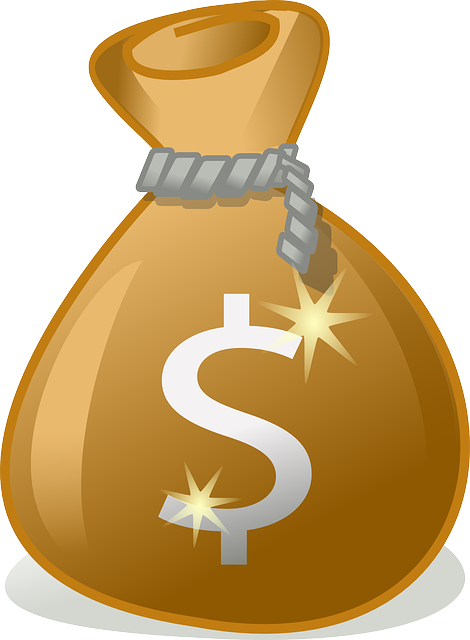 In 2021, its GDP grew by 0.00% [2]
In 2021, its GDP grew by 0.00% [2]
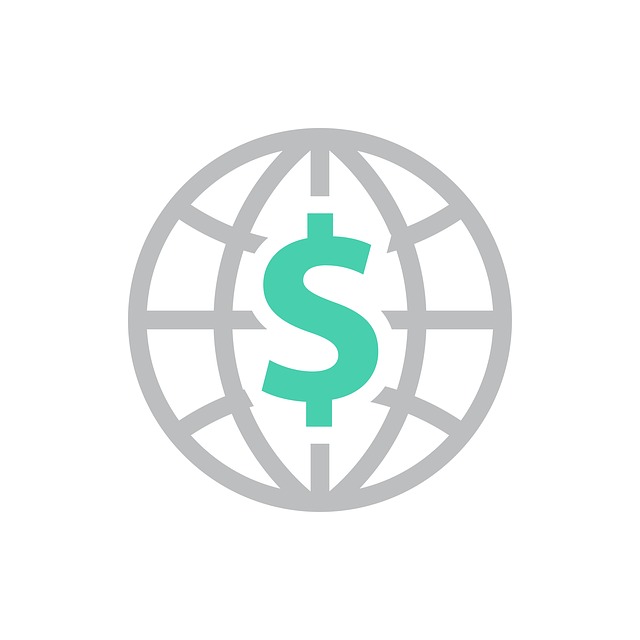 In 2021 it had a positive Current
In 2021 it had a positive Current
Account Balance of US$bn 0.00 [3]
What free trade areas or economic unions is it a member of?
None
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]What trade deals are there with other countries and economic unions?
India - Afghanistan partial scope agreement (from 13/05/2003)
South Asian Free Trade Agreement (from 01/01/2006)
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]Constant Improvement, Constant Investment — a Simple Recipe for Banking Success and Recognition
The Fog of War: The Tragic Triumph of Hope Over Experience – The Folly of Great Powers
Uzbekistan’s Dynamism Presents New Opportunities for Post-Brexit Britain
Sherzod Khodjhaev, Deputy Minister for Energy, Republic of Uzbekistan: Uzbekistan Gets to Grips with Challenges of Responsible Electric Power Generation
Q&A with CEO of Insurance Corporation of Afghanistan: Jamal Asfour
CFI.co Meets the President & CEO of Azizi Bank: Mohammad Salem Omaid
Kristalina Georgieva, CEO of the World Bank: Empowering Communities
Peter Carington: The Sole Survivor of a Bygone Era
CFI.co Meets the CEO of Makhtag: Muhammad Halim Fidai
United Nations Office for Project Services (UNOPS): Infrastructure to Empower Women
Trade with the United Kingdom
Source: UK Office for National Statistics, October 2022.
Contains public sector information licensed under the Open Government Licence v3.0.