The Two Sides of Capital Flows into Brazil
There was a significant inflow of funds in Brazil’s external financial account in October and November for investments in both stocks and fixed income instruments.
The bulk of the recent inflow has come in a passive way, and it did not include much volume on the side of active investors. For the wave to unfold in the availability of external resources to finance investments in the country, progress and confidence in the domestic fiscal and regulatory agenda will be relevant.
FDI in Brazil this year remains weak (Chart 1) but there was a significant inflow of funds in the external financial account in October and November for investments in stocks and fixed income instruments.
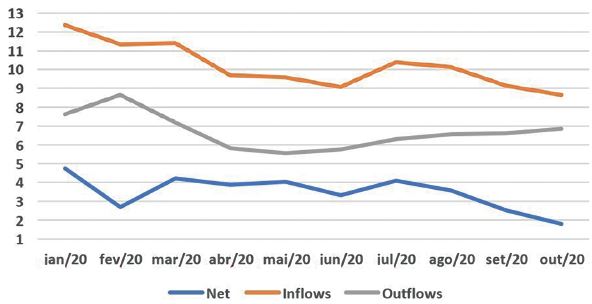
Chart 1: FDI monthly flows 2020 (USD $ billion). Source: Central Bank of Brazil
The portfolio investment account for the year remains in the red (Chart 2). The substantial departure in March and April, reflecting the tremendous shock that Covid-19 brought to the global financial markets, has not yet been fully offset by inflows since June. But for some, the recent figures gave rise to a feeling that the improvement in international financial conditions was sufficient to guarantee tranquility on the external front.
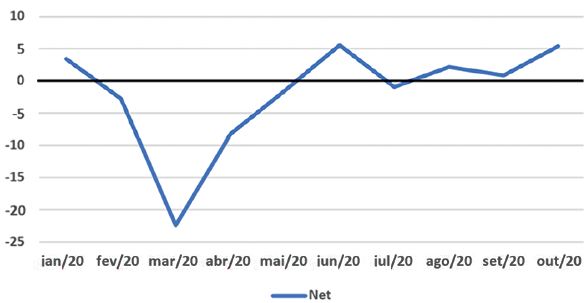
Chart 2: Portfolio investment – net flows 2020 (USD $ billion). Source: Central Bank of Brazil
The external inflow was an important factor for Brazil’s equity index (Ibovespa) to register an increase of 17.73 percent in November, which reduced the fall in 2020 to 4.35 percent. In dollars, due to the appreciation of the real in the month, the appreciation was almost 25 percent, placing the Brazilian stock exchange as the best performing of emerging economies and the three largest Wall Street indices (S&P 500, Nasdaq and Dow Jones). It is also worth noting that the share of foreign investors holding domestic public debt securities rose from 9.44 percent to 9.79 percent in October.
What now? Could those who drew so much attention to the need for advances on the domestic policy side be exaggerating? Wouldn’t the approval of reforms to facilitate compliance with the public spending ceiling be a precondition for relying on foreign financial resources in the recovery of Brazilian economic growth?
The truth is that capital flows to emerging economies respond to external, more general, and domestic, country-specific factors and impulses. They are always the combined result of both, which implies recognising that, at the limit, domestic factors make each country unique. In the current Brazilian scenario, it is not possible to fully rely on the evolution of international financial conditions.
Let’s look outside. News of effective vaccines with lower logistical requirements has fuelled optimism about the future of the global economy. The appetite for taking risks has increased, particularly given the prospect of prolonged low rates of return in low-risk applications. The US election outcome also contributed to this.
Then, in November, there was a rush towards assets in emerging economies, accompanied by another for stocks and debt securities in the US. In the case of emerging markets, there is a clear return to the situation prior to the Covid-19 financial shock and the capital flight in March.
Emerging stock funds attracted nearly $14bn in the second and third weeks of November, while $22bn moved to buy stocks of those countries in the same month. Debt securities from those countries were also acquired with intensity (Chart 3).
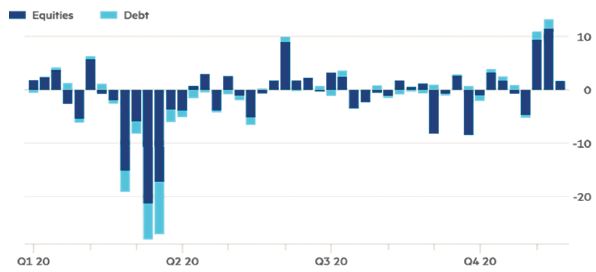
Chart 3: Cross-border flows have surged in two of the past three weeks.
Weekly foreign investor flows to local emerging markets (USD $ billion). Source: Institute of International Finance. © FT
The appetite for risk and the prospect of improvement in the global economy were manifested in a portfolio rotation, with a stronger demand for energy and financial services in relation to assets already valued in Wall Street. The Brazilian stock exchange as a destination benefited from the fact that it has banks, Vale and Petrobrás as main stocks.
There is also a forecast that the dollar will gradually devalue against other currencies. This tends to raise dividends and interest earned in local currencies with emerging assets in dollars, and facilitates the payment of debt commitments abroad by governments and companies in these countries. Just remember the hardships of some — like Argentina and Turkey in 2018 — in times of dollar appreciation.
The possibility that, at some point, the Federal Reserve will be urged to raise interest rates and/or undo its quantitative easing (QE) remains. The simple conjecture could generate a new “taper tantrum” like that of 2013, when the mere announcement by the Fed that it was planning to exit QE caused a huge outflow of capital from emerging countries with current account deficits, including Brazil at the time. In any case, this is not likely any time soon.
How about the country-specific side in the Brazilian case? First of all, it should be noted that the bulk of the recent inflow has come in a passive way, that is, as a component of funds that seek exposure to emerging assets in general. In this a group, Brazil occupies a significant position despite recent changes recent in indices. As an increasing volume of resources in the global financial markets has been driven by exchange traded funds (ETFs), in relative terms, lower quality assets (lower-rated sovereign bonds, less liquid stock markets) undergo more positive and negative impacts than the others in situations of increase or decrease in the size of ETFs.
The recent inflow of capital in Brazil did not include considerable volume on the side of active investors, those who look directly at specific assets. For these, country-specific domestic determinants weigh more. For the ongoing positive wave to unfold in the availability of external resources to finance investments in the country, progress and confidence in the domestic fiscal and regulatory agenda will be relevant.
Public-private partnerships, as fiscal space for public investments, will continue to be tight in the coming years. As the inflow of funds is no longer obtained by offering high interest premiums on the public debt, its full return will have to occur for exposure to assets of another nature. Many think that the Brazilian economy is at a crossroad, with possible positive or negative trajectories in the interaction between risk premiums, interest, public debt and GDP. Capital inflows or outflows will respectively reinforce positive and negative trajectories. And the homework will make a difference.
You may have an interest in also reading…
UN Labour Report Shows Solid Return for National Investments in Quality Jobs
Developing countries that invested in quality jobs from the early 2000s grew nearly one percentage point faster every year since
Brazil Has Reason to be Proud of First-Tier Banks
Reported by Marcos dos Santos. After a period of tension between the banking sector and the Brazilian government, the Executive
EY on COVID-19 Pandemic: An Opportunity for Reinvention of Family Enterprises
Family businesses and SMEs face great challenges, as well as personal and financial losses, in these turbulent times. On the
















































































